Example.
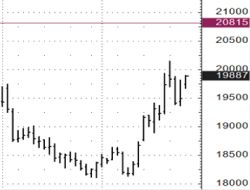
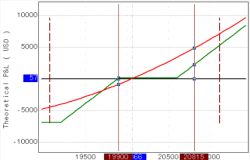
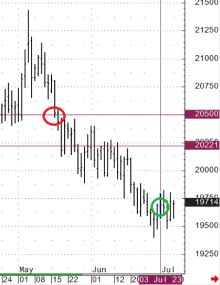
"Gap". Oil futures.
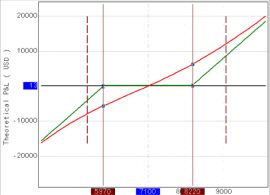
There is a short position in a futures (sold futures). The stop order is at 76.00, limiting potential losses. However, significant news came out over the weekend and the market opened with a “gap” and the stop order was executed at a price of 80.10, realizing additional losses. If, instead of a stop order at 76.00, a call option with a strike price of 76.00 had been purchased, it would have guaranteed the position to be closed at 76.00. In this case, the maximum additional loss would be limited only by the option premium, which would be significantly better compared to an executed stop order at a price of 80.10. Moreover, since using an option as a “stop loss” there is no need to close the position, there was still a chance (if there was enough time before the option expiration) to wait for the fall and realize the profit as a result.